LangChain Code#
Use the LangChain Code node to import LangChain. This means if there is functionality you need that n8n hasn't created a node for, you can still use it. By configuring the LangChain Code node connectors you can use it as a normal node, root node or sub-node.
On this page, you'll find the node parameters, guidance on configuring the node, and links to more resources.
Not available on Cloud
This node is only available on self-hosted n8n.
Node parameters#
Add Code#
Add your custom code. Choose either Execute or Supply Data mode. You can only use one mode.
Unlike the Code node, the LangChain Code node doesn't support Python.
- Execute: use the LangChain Code node like n8n's own Code node. This takes input data from the workflow, processes it, and returns it as the node output. This mode requires a main input and output. You must create these connections in Inputs and Outputs.
- Supply Data: use the LangChain Code node as a sub-node, sending data to a root node. This uses an output other than main.
By default, you can't load built-in or external modules in this node. Self-hosted users can enable built-in and external modules.
Inputs#
Choose the input types.
The main input is the normal connector found in all n8n workflows. If you have a main input and output set in the node, Execute code is required.
Outputs#
Choose the output types.
The main output is the normal connector found in all n8n workflows. If you have a main input and output set in the node, Execute code is required.
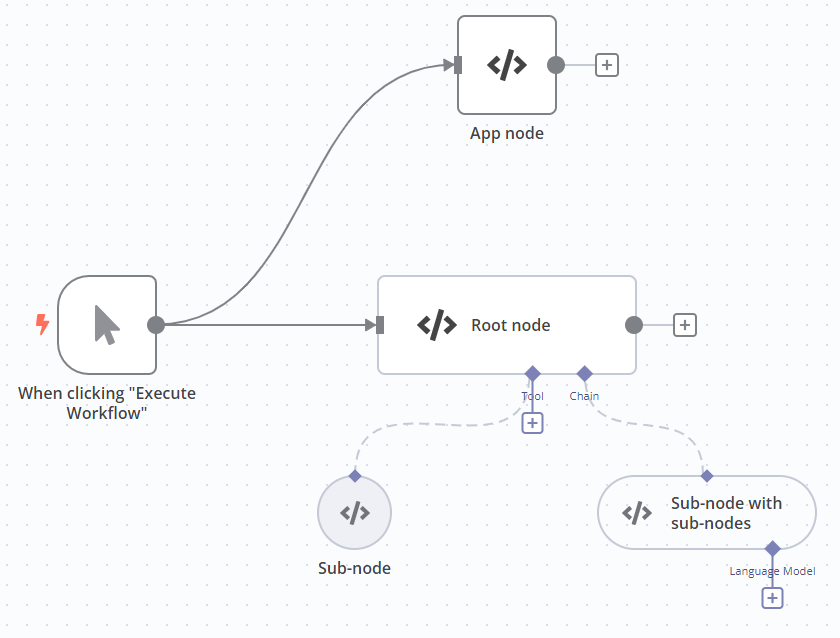
Node inputs and outputs configuration#
By configuring the LangChain Code node connectors (inputs and outputs) you can use it as an app node, root node or sub-node.
| Node type | Inputs | Outputs | Code mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| App node. Similar to the Code node. | Main | Main | Execute |
| Root node | Main; at least one other type | Main | Execute |
| Sub-node | - | A type other than main. Must match the input type you want to connect to. | Supply Data |
| Sub-node with sub-nodes | A type other than main | A type other than main. Must match the input type you want to connect to. | Supply Data |
Built-in methods#
n8n provides these methods to make it easier to perform common tasks in the LangChain Code node.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
this.addInputData(inputName, data) |
Populate the data of a specified non-main input. Useful for mocking data.
|
this.addOutputData(outputName, data) |
Populate the data of a specified non-main output. Useful for mocking data.
|
this.getInputConnectionData(inputName, itemIndex, inputIndex?) |
Get data from a specified non-main input.
|
this.getInputData(inputIndex?, inputName?) |
Get data from the main input. |
this.getNode() |
Get the current node. |
this.getNodeOutputs() |
Get the outputs of the current node. |
this.getExecutionCancelSignal() |
Use this to stop the execution of a function when the workflow stops. In most cases n8n handles this, but you may need to use it if building your own chains or agents. It replaces the Cancelling a running LLMChain code that you'd use if building a LangChain application normally. |
Templates and examples#
Related resources#
View n8n's Advanced AI documentation.
- completion: Completions are the responses generated by a model like GPT.
- hallucinations: Hallucination in AI is when an LLM (large language model) mistakenly perceives patterns or objects that don't exist.
- vector database: A vector database stores mathematical representations of information. Use with embeddings and retrievers to create a database that your AI can access when answering questions.
- vector store: A vector store, or vector database, stores mathematical representations of information. Use with embeddings and retrievers to create a database that your AI can access when answering questions.